SERVICES
Myofascial Trigger Point Acupuncture
Electro-Acupuncture / Percutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
Cupping / Negative Pressure Myofascial Decompression
Electro-Cupping (cupping + transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation)
Thermal Guasha / Instrument-Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization
Photobiomodulation aka Red Light & Near Infrared Light Therapy
Infrared Negative Ion Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy
Sequential Compression Therapy
ORTHOPEDIC & SPORTS MEDICINE ACUPUNCTURE
Orthopedic and sports medicine acupuncture are specialized approaches that address musculoskeletal challenges and support physical goals. Orthopedic acupuncture focuses on conditions such as chronic pain, arthritis, post-surgical recovery, and soft tissue issues, reducing inflammation, improving joint mobility, and promoting healing in muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves. It effectively manages degeneration, imbalances, and injuries. Sports medicine acupuncture targets strains, sprains, joint dysfunction, and overuse injuries, enhancing performance, accelerating recovery, and optimizing muscle function for athletes of all levels, from casual enthusiasts to professionals.
This practice integrates modern adaptations of traditional acupuncture with Western orthopedic insights to create practical, tailored treatment plans. Techniques like motor point acupuncture, myofascial trigger point acupuncture, and electro-acupuncture address muscle tension, pain, and nerve balance. Sessions begin with a detailed assessment—evaluating posture, movement, and history—to identify needs and objectives. Advanced training in anatomy and biomechanics informs the approach, improving movement, strength, and overall function.
MOTOR POINT ACUPUNCTURE
Motor points are precise locations where needle insertion targets neuromuscular junctions, where nerves connect with muscle fibers. This technique uses anatomical knowledge and skilled palpation to stimulate these spots. It resets muscle function by activating weak, inhibited fibers to improve strength and responsiveness, while releasing tension in overworked, tight muscles to enhance flexibility and reduce strain. The needling boosts local blood flow and oxygen delivery, supports tissue healing by aiding repair processes, and reduces inflammation and pain through neural modulation. This approach expands range of motion and improves coordination and muscle efficiency by optimizing nerve-muscle interaction.
MYOFASCIAL TRIGGER POINT ACUPUNCTURE / DRY NEEDLING
Trigger points are tight, sensitive muscle areas causing pain, stiffness, or tingling, often due to tension and restricted blood flow. They arise from strain, overuse, poor posture, and injury. This needling technique targets these fibers to relieve discomfort, increase mobility, and improve muscle function. Paired with motor point acupuncture, it releases tension, boosts circulation, and supports healing, addressing both localized and referred pain effectively.
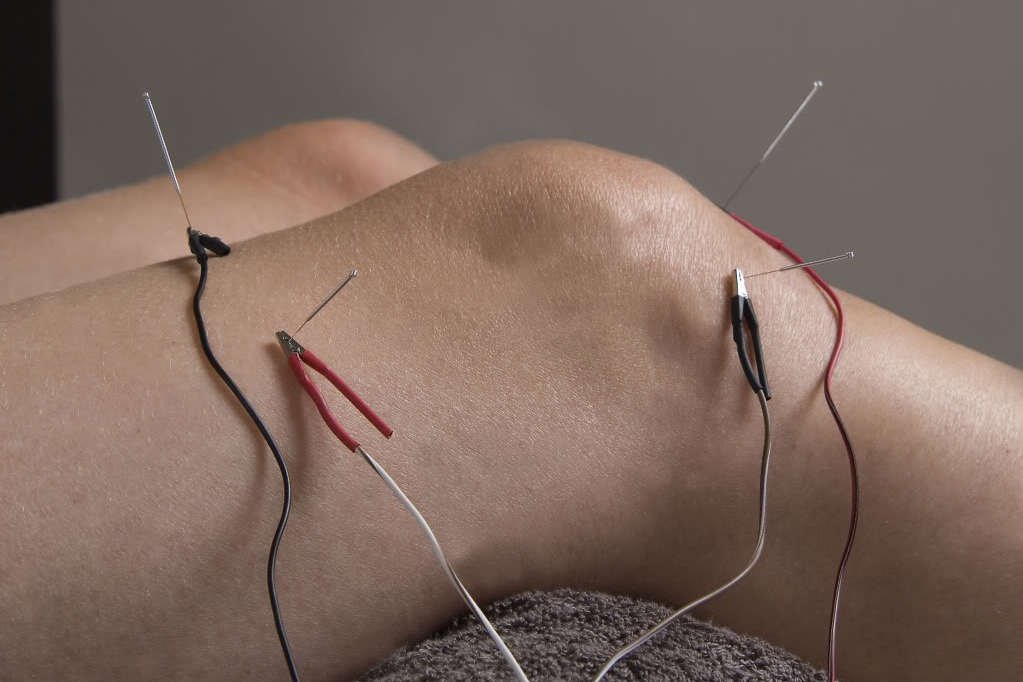
ELECTRO-ACUPUNCTURE (Percutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
Electro-acupuncture applies gentle electrical currents to needles, enhancing therapeutic outcomes. The current, adjusted in frequency and intensity, reduces pain, inflammation, and muscle tension while boosting circulation and healing. It also improves sensorimotor integration—connecting sensation to movement—for better coordination and recovery. This modern adaptation amplifies traditional methods, targeting specific areas for optimal results.
CUPPING / MYOFASCIAL DECOMPRESSION
Cupping uses suction cups to lift fascial layers and increase blood flow to tense or painful muscles. It reduces pain, inflammation, and stiffness while improving range of motion. Effective for sports injuries and joint discomfort, it promotes tissue relaxation and accelerates recovery through enhanced circulation.
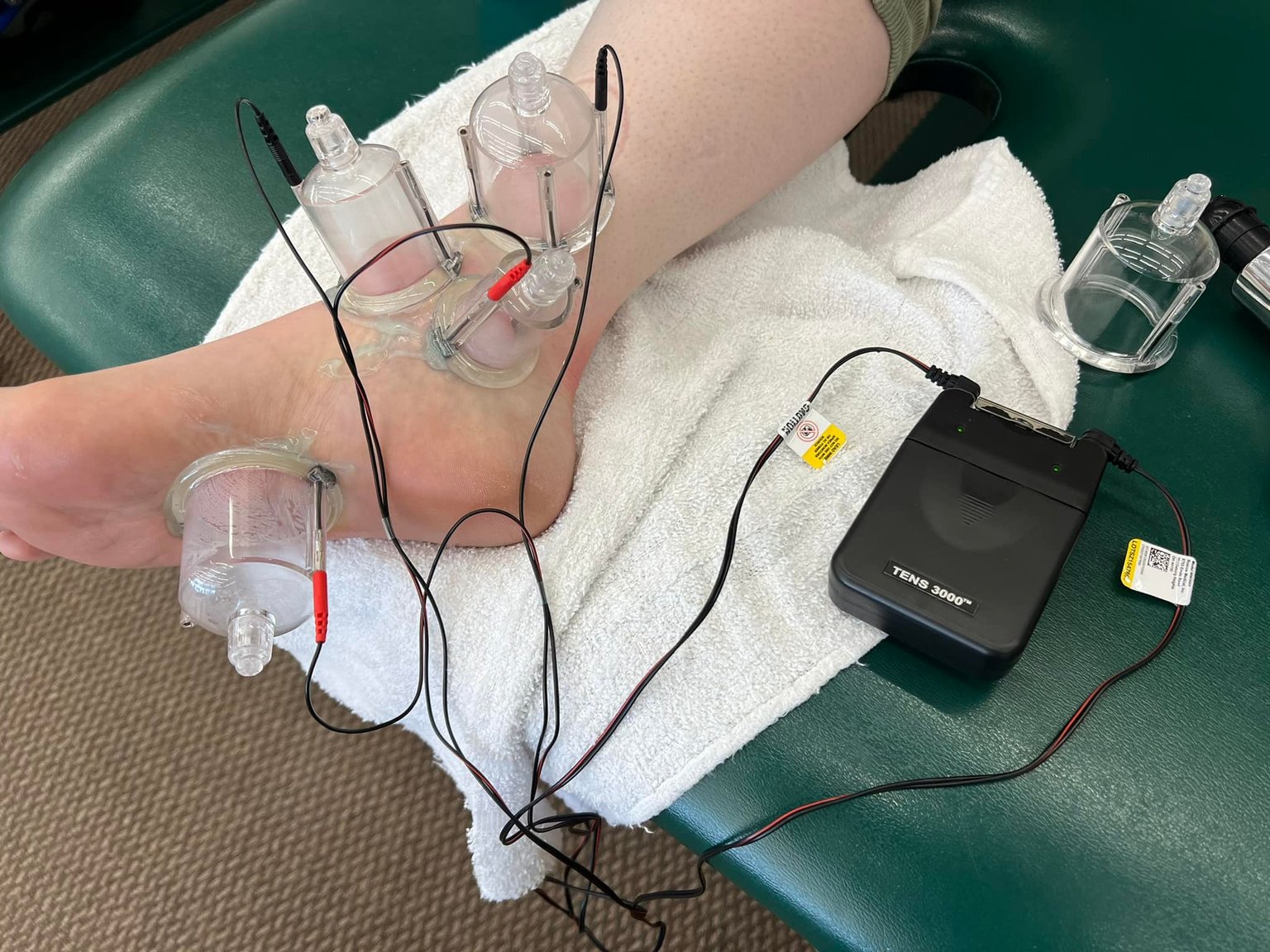
ELECTRO-CUPPING (Myofascial Decompression + Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
Electro-cupping combines suction with electrical stimulation, targeting fascia and muscle tissue. The adjustable frequency promotes relaxation or healing, addressing pain, supporting injury recovery, and enhancing performance. This dual method boosts circulation and tissue repair for comprehensive musculoskeletal relief.
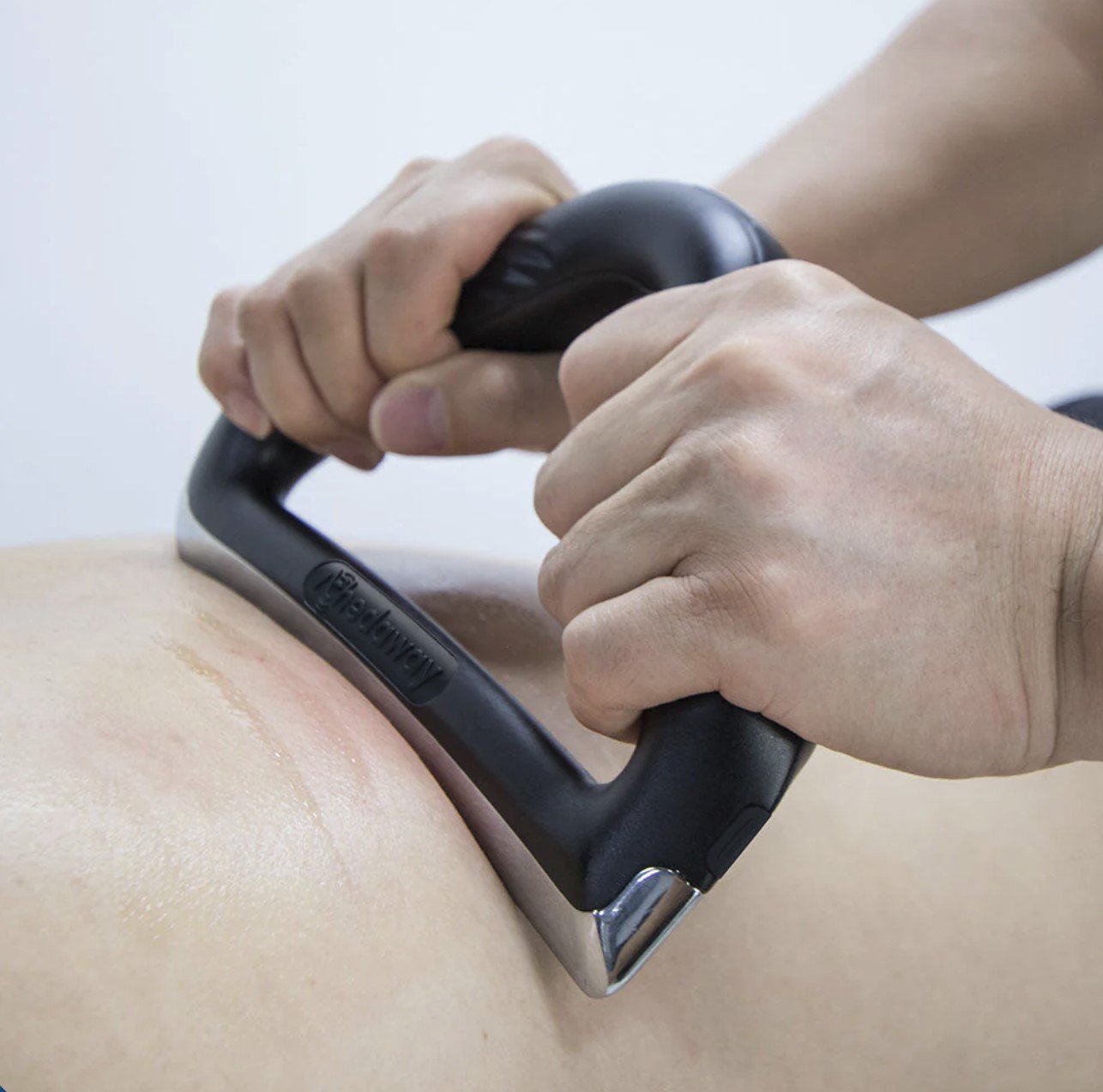
GUA SHA / INSTRUMENT-ASSISTED SOFT TISSUE MOBILIZATION (IASTM)
Gua Sha employs tools to break up tissue restrictions and adhesions in soft tissues. Applied to painful or immobile areas, it reduces inflammation and enhances flexibility, particularly for tendinopathies or strains. Often paired with other treatments, it improves tissue health and alleviates discomfort efficiently. By promoting blood flow and stimulating the body’s natural healing processes, Gua Sha can accelerate recovery and restore optimal function in affected areas.
PHOTOBIOMODULATION (Red & Near Infrared Light Therapy)
Photobiomodulation uses red and near-infrared light (600-1000 nm wavelengths) to energize cells, improve blood flow, and speed up healing. Delivered with low-level lasers or LEDs, it works by boosting energy production in cells—specifically adenosine triphosphate (ATP)—through a key enzyme in the mitochondria. This helps repair tissues faster, calms inflammation by lowering signals like IL-6, and eases pain naturally. The light reaches 1-2 cm into muscles or joints, opening blood vessels with nitric oxide to bring more oxygen and nutrients. It’s a gentle, non-invasive way to reduce fatigue, support recovery, and improve comfort in musculoskeletal and neurological conditions.
PULSED ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD THERAPY (PEMF)
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF) sends low-frequency electromagnetic pulses (1-100 Hz) to encourage healing and wellness. It interacts with cells by fine-tuning their electrical balance, helping nutrients like calcium move more easily and sparking repair signals inside. This process builds stronger tissues, improves blood flow through tiny vessels, and tones down inflammation by adjusting natural chemicals like prostaglandins. Applied to specific spots or the whole body, it reduces pain, supports recovery from issues like arthritis or fibromyalgia, and enhances circulation. It’s a safe, supportive method that recharges cells and promotes musculoskeletal health when used properly..
NORMATEC DYNAMIC AIR COMPRESSION RECOVERY SYSTEM
NormaTec employs dynamic air compression to improve circulation and speed recovery in the limbs. Using inflatable sleeves, it massages muscles in a wave-like pattern, reducing swelling, soreness, and fatigue after exercise or injury. Sequential compression enhances lymphatic drainage and clears metabolic waste effectively. The system applies pressure in stages—starting at the feet and moving upward—to mimic the body’s natural fluid flow. This helps flush out lactic acid buildup and supports quicker muscle repair, making it especially useful for intense physical activity or post-injury relief.
POSTURAL & FUNCTIONAL ASSESSMENT WITH CORRECTIVE EXERCISES
Postural and functional assessments evaluate alignment and movement to identify imbalances or limitations. These analyze stance, flexibility, and coordination to address issues like back or joint pain. Corrective exercises strengthen weak areas, stretch tight muscles, and improve overall function, enhancing performance and reducing discomfort through targeted adjustments. The process often involves observing how the body holds itself during rest and activity, spotting uneven patterns like slouched shoulders or tilted hips. Tailored movements then retrain the body, helping restore balance and ease strain over time.
Post-Surgery Recovery
Acupuncture is a beneficial therapeutic modality to enhance post-surgery recovery by addressing both the physiological and symptomatic aspects of healing. It helps in the reduction of post-operative pain through the stimulation of endogenous analgesic systems, including the release of endorphins and enkephalins, which provide pain relief. Acupuncture also promotes blood circulation to the affected areas, facilitating the delivery of nutrients and oxygen essential for tissue repair and regeneration. Additionally, it reduces inflammation by modulating the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn helps minimize swelling and discomfort at the surgical site. Acupuncture can accelerate healing time by promoting cell regeneration and optimizing collagen production, essential for wound healing and tissue remodeling. Moreover, it plays a crucial role in enhancing immune function, assisting in the reduction of infection risks. These combined effects make acupuncture an invaluable adjunct to surgical recovery, supporting both the body’s natural healing processes and improving overall recovery outcomes.
Post-Stroke Recovery
Acupuncture supports post-stroke recovery by tackling muscle stiffness and boosting movement in a natural, science-supported way. It helps reduce spasticity—tight, overactive muscles—by triggering the release of endorphins and calming signals in the nervous system. Acupuncture also improves blood flow to the brain, delivering oxygen and nutrients that fuel neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to rewire and heal after a stroke. It eases swelling and discomfort by lowering inflammation, specifically through reducing cytokines like TNF-α. Plus, it enhances sensorimotor integration, strengthening how your senses and movements work together for better balance and coordination. By supporting brain repair and recovery, acupuncture speeds up the process. It’s a powerful addition to rehab, helping your body heal naturally and improving your overall progress.
Post-Concussion Recovery
Acupuncture helps post-concussion syndrome (PCS) patients manage symptoms like headaches, dizziness, fatigue, cognitive fog, and mood swings after a mild brain injury. Though not a cure, it offers relief through scientific mechanisms. Headaches ease as acupuncture triggers endorphin release and blocks pain signals via spinal pathways, reducing medication needs. Dizziness improves with enhanced cerebral blood flow—via nitric oxide vasodilation—and vestibular regulation. Cognitive fog clears as it boosts prefrontal perfusion and balances serotonin and dopamine. Fatigue lessens by stabilizing the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, cutting cortisol levels. Emotionally, it calms limbic overactivity and stress hormones, reducing anxiety. It also curbs neuroinflammation by lowering oxidative stress, as seen in brain injury research. Sleep improves with melatonin increases and sympathetic suppression, supporting repair. Autonomic balance shifts, easing sensory overload. Starting 1-2 weeks post-injury with weekly sessions, acupuncture’s benefits for pain and stress are study-backed, providing a low-risk complement to therapies like rehab, helping patients recover more comfortably.
Sports Performance Enhancement
Acupuncture enhances athletic performance by improving muscle strength, endurance, and flexibility. It stimulates specific points to optimize neuromuscular function, increasing muscle coordination and strength. Acupuncture also regulates the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, helping the body transition from a stress state to a recovery state. This speeds up muscle repair, reduces lactic acid buildup, and promotes quicker recovery. By improving blood circulation, acupuncture enhances the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to muscles and helps clear metabolic waste, reducing muscle soreness and inflammation. This process not only accelerates recovery time but also improves joint mobility and flexibility, essential for ongoing performance. Acupuncture is a powerful tool to help athletes break through performance plateaus and enhance their training results.
Back Injuries
We treat both sudden (acute) and long-term (chronic) lower back pain, including muscle strains, sprains, and joint issues such as facet joint and sacroiliac (SI) joint pain. Conditions like degenerative disc disease (spondylosis), herniated or bulging discs, and sciatica (nerve pain radiating down the leg) are also addressed. Additionally, we manage stenosis, the narrowing of spaces within the spine or nerve passages, which can lead to nerve compression and cause pain, numbness, or weakness. We also treat bone spurs (osteophytes) that contribute to stiffness and discomfort, as well as conditions like spondylolisthesis (vertebrae slipping out of place), mid-back pain, general thoracic spine discomfort, and more.
Head & Neck Injuries
We help manage neck pain caused by muscle spasms, joint problems, and injuries resulting from sudden movements (e.g., whiplash). Degenerative issues affecting the neck, like spondylosis, as well as conditions such as disc injuries and stenosis (narrowing of spaces within the neck or nerve passages) are also treated. We also address the formation of bone spurs in the cervical spine, which can lead to stiffness, pain, and reduced range of motion. Additional conditions include tension headaches, migraines, and facial nerve pain (e.g., trigeminal neuralgia). We also provide care for jaw issues (TMD), facial weakness and paralysis (Bell's palsy), recovery from strokes, lingering symptoms after a concussion, and more.
Shoulder Injuries
We provide treatment for frozen shoulder, rotator cuff issues, and general shoulder pain from overuse or injury, including impingement syndromes. Additionally, we address conditions such as labral tears, biceps tendon problems, and arthritis. Nerve compression syndromes like thoracic outlet syndrome and shoulder stiffness from limited rotation are also managed. Other common shoulder conditions we treat include bursitis, tendinopathy, AC joint dysfunction, and scapular dyskinesis, all with a focus on restoring function, reducing pain, and improving mobility.
Hip Injuries
We treat hip flexor and groin strains, hip joint pain, and arthritis. Additionally, we address femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), labral tears, gluteal tendon issues, bursitis, and deep gluteal conditions like piriformis syndrome, which can cause sciatica-like symptoms. Other common hip disorders we manage include hip instability, snapping hip syndrome, and nerve entrapments (e.g., lateral femoral cutaneous, femoral, obturator), all with a focus on restoring mobility, reducing pain, and improving overall function.
Thigh & Knee Injuries
We treat hamstring strains, runner’s knee (patellofemoral syndrome), jumper’s knee (patellar tendinopathy), IT band syndrome, meniscus injuries, and ligament tears (e.g., ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL). Degenerative changes in the knee joint, such as osteoarthritis, are also addressed. This condition involves the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion. Symptoms of knee arthritis, including discomfort and limited mobility due to these degenerative changes, are managed with therapies aimed at improving function and alleviating pain. We also treat Baker’s cysts and fibular head misalignment.
Leg, Ankle, & Foot Injuries
We manage ankle sprains, shin splints, calf strains, and Achilles tendon issues. Other conditions treated include peroneal tendon problems, plantar fasciitis/fasciosis, posterior tibialis tendinopathy, Morton’s neuroma, stress fractures, tarsal tunnel syndrome, and arthritis in the foot and ankle. Additionally, we address heel spurs, sesamoiditis, cuboid syndrome, metatarsalgia, and other nerve entrapments that affect foot function and mobility.
Elbow & Forearm Injuries
We address conditions such as tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis), golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis), ligament sprains, triceps tendon issues, and olecranon bursitis. Nerve compression problems, such as cubital tunnel syndrome, as well as arthritis in the elbow, are also managed.
Wrist, Hand, & Finger Injuries
We treat wrist tendinitis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and thumb tendon issues such as De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. Other conditions addressed include trigger finger, finger pulley injuries, TFCC tears in the wrist, ganglion cysts, arthritis in the wrist and hand, and CMC (carpometacarpal) joint pain, which can cause discomfort at the base of the thumb, often due to degenerative changes or osteoarthritis.